At Tembo, we’ve been developing an open-source Kubernetes Operator for Postgres. We use this operator to power our managed Postgres platform, Tembo Cloud. We’re excited to share our progress, experience, and vision for this project. This post aims to assist anyone interested in utilizing Kubernetes operators for Postgres or writing Kubernetes operators using Rust.
What is a Kubernetes Operator?
Kubernetes was designed with automation in mind, and operators allow for users to extend native Kubernetes behavior and principles to manage custom resources and components.
With a Kubernetes operator, users can write code that defines how their application should be deployed and managed on Kubernetes. This code is then packaged into a container image and deployed to Kubernetes. The operator then watches for changes to the custom resource and takes action to reconcile the state of the application’s components with the desired state of the custom resource.
In short, using a Kubernetes operator is the most effective way to run applications on Kubernetes in 2023.
You can read more about Kubernetes operators on this CNCF blog post, where the image below is.
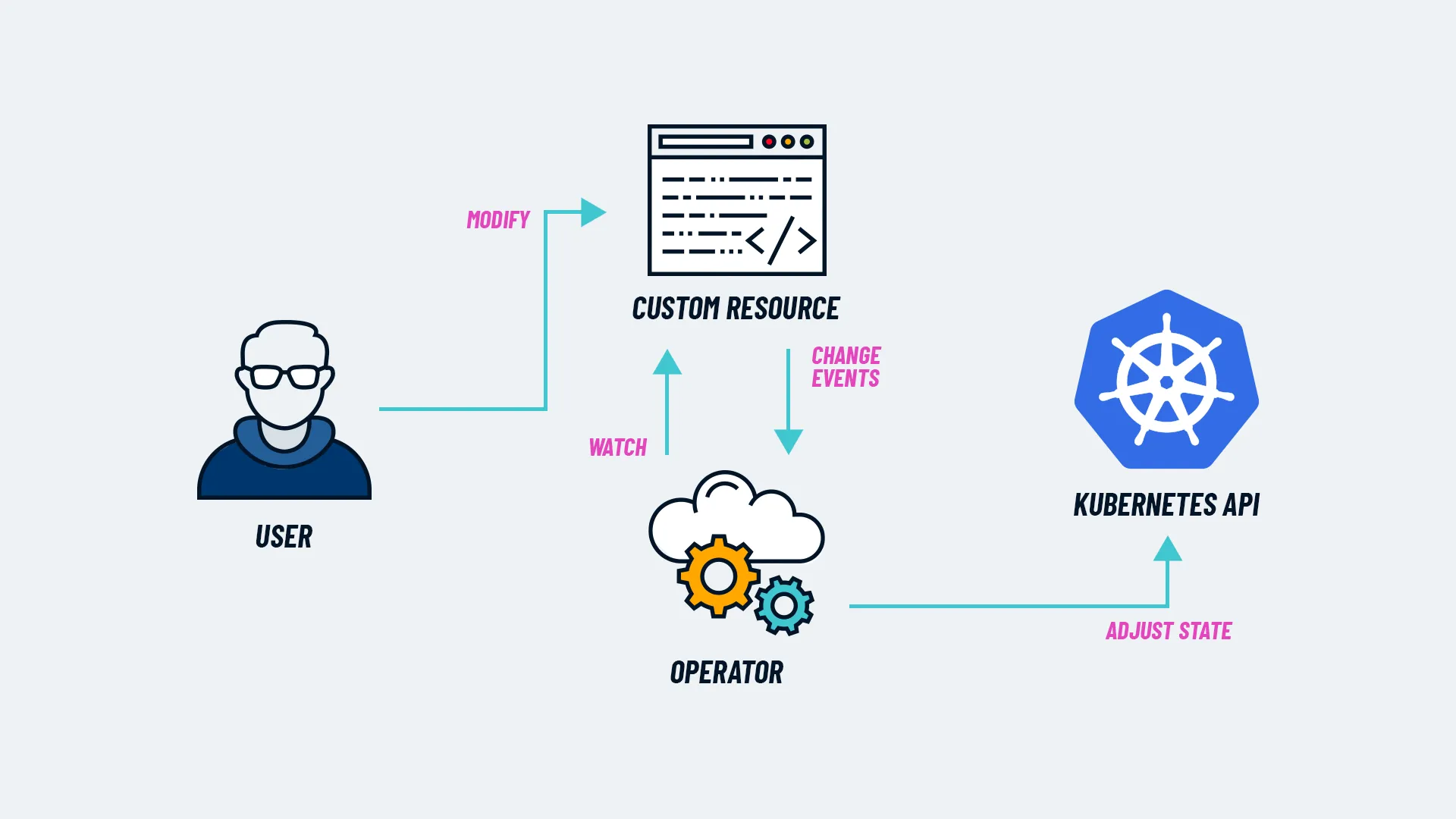
*Image credit: CNCF blog*
Kubernetes Operators and the Rise of Rust
Because Kubernetes itself is written in Go, the majority of Kubernetes operators available today are also written in Go. The kubebuilder project simplifies the process of building Kubernetes operators in Go and is widely considered the de facto standard for doing so.
With the increasing popularity of Rust, it was only a matter of time before someone developed a framework for building Kubernetes operators in Rust. The kube-rs project allows developers to build Rust-based Kubernetes operators in a similar manner to the kubebuilder project. This project excited us for a few reasons:
- We were interested in learning Rust.
- We wanted to explore whether Rust could be a viable alternative to Go for writing Kubernetes operators.
- We were inspired by the success of companies like Stackable, who have developed numerous Kubernetes operators in Rust.
This excitement led us to the decision to write our Kubernetes operator in Rust.
Building the Tembo Operator
Tembo Cloud distinguishes itself from other managed Postgres offerings in several ways, one of which is the ability to install and enable Postgres extensions on the fly. This experience is in part powered by Trunk, a Postgres extension registry and companion CLI that provide a simplified extension management experience.
It also introduces the concept of Stacks, which are pre-built use-case-specific Postgres deployments which are optimized and tuned to serve a specific workload.
Roll Your Own
In order to build these unique capabilities, we knew we’d need to harness the power and flexibility of a Kubernetes operator in our own way. Although there are several Kubernetes operators for Postgres available, none of them offer the same unique Postgres extension management experience or the concept of Stacks.
Initially, we attempted to build our own operator from scratch. We had successfully built the extension management piece, but soon realized that we were duplicating existing efforts. We had a comprehensive list of baseline features to develop, which included:
- Backup
- Recovery
- Connection Pooling
- Failover
- Upgrades
CNPG to the Rescue
Enter CloudNativePG (CNPG). CNPG is a Kubernetes operator for Postgres created by the folks at EDB. We found it to be the most compelling of the many Kubernetes operators for Postgres out there. It provided many of the features we needed, including backup, recovery, connection pooling, failover, and upgrades. However, we still needed the ability to install and enable any Postgres extensions on the fly and define Stacks.
This is where the Tembo Operator comes in. We built the Tembo Operator in a way that utilizes CNPG, which enables us to offer a distinctive management experience for Postgres extensions and Stacks while utilizing a reliable and stable Postgres solution.
Using the Tembo Operator
Let’s take a look at what a custom resource spec looks like for the Tembo Operator. Here’s an example for our Machine Learning Stack. We can see this sample spec makes use of our Machine Learning Stack and includes a handful of extensions. Keep in mind, these extensions are installed at runtime with Trunk and are not built into the container image.
apiVersion: coredb.io/v1alpha1
kind: CoreDB
metadata:
name: sample-machine-learning
spec:
image: "quay.io/tembo/ml-cnpg:15.3.0-1-a3e532d"
stop: false
stack:
name: MachineLearning
postgres_config:
- name: pg_stat_statements.track
value: all
- name: cron.host
value: /controller/run
- name: track_io_timing
value: 'on'
- name: shared_preload_libraries
value: vectorize,pg_stat_statements,pgml,pg_cron,pg_later
trunk_installs:
- name: pgvector
version: 0.5.0
- name: pgml
version: 2.7.1
- name: pg_embedding
version: 0.1.0
- name: pg_cron
version: 1.5.2
- name: pgmq
version: 0.14.2
- name: vectorize
version: 0.0.2
- name: pg_later
version: 0.0.8
extensions:
# trunk project pgvector
- name: vector
locations:
- database: postgres
enabled: true
version: 0.5.0
# trunk project postgresml
- name: pgml
locations:
- database: postgres
enabled: true
version: 2.7.1
# trunk project pg_embedding
- name: embedding
locations:
- database: postgres
enabled: false
version: 0.1.0
- name: pg_cron
description: pg_cron
locations:
- database: postgres
enabled: true
version: 1.5.2
- name: pgmq
description: pgmq
locations:
- database: postgres
enabled: true
version: 0.14.2
- name: vectorize
description: simple vector search
locations:
- database: postgres
enabled: true
version: 0.0.2
- name: pg_later
description: async query execution
locations:
- database: postgres
enabled: true
version: 0.0.8
runtime_config:
- name: shared_buffers
value: "1024MB"
- name: max_connections
value: "431"
- name: work_mem
value: "5MB"
- name: bgwriter_delay
value: "200ms"
- name: effective_cache_size
value: "2867MB"
- name: maintenance_work_mem
value: "204MB"
- name: max_wal_size
value: "10GB"To create our Postgres instance, we run the following command:
$ kubectl apply -f yaml/sample-machine-learning.yaml
coredb.coredb.io/sample-machine-learning created
$ kubectl get po
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
sample-machine-learning-1 1/1 Running 0 19s
sample-machine-learning-metrics-5fbcf9b676-hkxtk 1/1 Running 0 31sOnce we’ve connected to the Postgres instance, we can run \dx to confirm the extensions were installed and enabled as expected:
$ export PGPASSWORD=$(kubectl get secrets/sample-machine-learning-connection --template={{.data.password}} | base64 -d)
$ psql postgres://postgres:$PGPASSWORD@sample-machine-learning.localhost:5432
psql (16.0 (Ubuntu 16.0-1.pgdg22.04+1), server 15.3)
SSL connection (protocol: TLSv1.3, cipher: TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, compression: off)
Type "help" for help.
postgres=# \dx
List of installed extensions
Name | Version | Schema | Description
--------------------+---------+------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------
pg_cron | 1.5 | pg_catalog | Job scheduler for PostgreSQL
pg_later | 0.0.8 | pglater | pg_later: Run queries now and get results later
pg_stat_statements | 1.10 | public | track planning and execution statistics of all SQL statements executed
pgmq | 0.14.2 | public | A lightweight message queue. Like AWS SQS and RSMQ but on Postgres.
plpgsql | 1.0 | pg_catalog | PL/pgSQL procedural language
vector | 0.5.0 | public | vector data type and ivfflat access method
vectorize | 0.0.2 | vectorize | The simplest way to do vector search on PostgresLet’s install a new extension by adding the following to our sample spec:
...
trunk_installs:
- name: pg_bm25
version: 0.4.0
...
extensions:
- name: pg_bm25
locations:
- database: postgres
enabled: true
version: 0.4.0After applying the updated spec and connecting to Postgres, we can see the new extension pg_bm25 is installed and enabled as expected:
$ psql postgres://postgres:$PGPASSWORD@sample-machine-learning.localhost:5432
psql (16.0 (Ubuntu 16.0-1.pgdg22.04+1), server 15.3)
SSL connection (protocol: TLSv1.3, cipher: TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, compression: off)
Type "help" for help.
postgres=# \dx
List of installed extensions
Name | Version | Schema | Description
--------------------+---------+------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------
pg_bm25 | 0.0.0 | paradedb | pg_bm25: PostgreSQL-native, full text search using BM25
pg_cron | 1.5 | pg_catalog | Job scheduler for PostgreSQL
pg_later | 0.0.8 | pglater | pg_later: Run queries now and get results later
pg_stat_statements | 1.10 | public | track planning and execution statistics of all SQL statements executed
pgmq | 0.14.2 | public | A lightweight message queue. Like AWS SQS and RSMQ but on Postgres.
plpgsql | 1.0 | pg_catalog | PL/pgSQL procedural language
vector | 0.5.0 | public | vector data type and ivfflat access method
vectorize | 0.0.2 | vectorize | The simplest way to do vector search on PostgresUp Next
We’re currently working on exciting new features that enable the deployment of custom applications alongside Postgres. These features include a REST API, GraphQL, and more. Stay tuned for future updates!
For more information on running the Tembo Operator, check out our docs at:
If you’re interested in contributing to the project, check out our Github repo at:
And if you want to try out the full power of Postgres and fully delegate extension management to us, try out Tembo Cloud.
